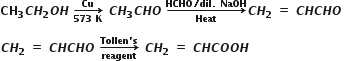Chemistry Ii Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones And Carboxylic Acids
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 12 Home%252bscience Chemistry Ii
Write the structures of the following compounds.
2-Hydroxycyclopentane carbaldehyde
2-Hydroxycyclopentane carbaldehyde

Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points:
CH3CHO, CH3CH2OH, CH3OCH3, CH3CH2CH3.
The high boiling points of alcohols are mainly due to the presence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding in them which is lacking in ethers and hydrocarbons.
Therefore their incereasing order of boiling point;
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions:
Ethanal, Propanal, Propanone, Butanone.

The electron density at the carbonyl carbon increase with the increase in the +I effect. The + I effect of the alkyl group increases in the order:
Ethanal < propanal < propanone < Butanone
As a result, the chances of attack by a nucleophilie decrease. Hence, the increasing order of the reactivates of the given carbonyl compounds in nucleophilic addition reaction is:
Butanone < Propanone < Propanal < Ethanal.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions:
Benzaldehyde, p-Tolualdehyde, p-Nitrobenzaldehyde, Acetophenone.

The +I effect is more in ketone than in aldehyde. Hence, acetphenone is the least reactive in nucleophilic addition reaction. Among aldehyde, the +l effects is the highest in p-tolualdehyde because of the presence of the electron donating –CH3 group and the lowest in p-nitro bezaldehyde because of the presence of the electron withdrawing –NO2 group. Hence, the increasing order of the reactivates of the given as;
Acetophenone < p-Tolualdehyde < Benzaldehyde < p-Nitrobenzaldehyde.Sponsor Area
Show how each of following compounds could be converted to benzoic acid.
Ethylbenzene.
Benzoic acid can be prepared by vigrous oxidation of ethylbenzene with alkaline potassium permanganate.
Show how each of following compounds could be converted to benzoic acid.
Acetophenone.
Benzoic acid can prepared by vigrous oxidation of acetophenone with alkaline potassium permanganate.
Show how each of following compounds could be converted to benzoic acid.
Bromobenzene.
Bromobenzene react with magnesium in presence of ether forming a grignard reagents. gringnard reagent react with carbon dioxide to form salts of carboxylic acids which in turn give corresponding acids.
Show how each of following compounds could be converted to benzoic acid.
Phenylethene (styrene)
Phenylethene by reduction gives ethylbenzene. Ethylbenzene on vigrous oxidation with alkaline potassium permangante gives benzoic acid.

Which acid of each pair shown here would you expect to be stronger?
CH2FCOOH or CH2ClCOOH
Which acid of each pair shown here would you expect to be stronger?

Electron withdrawing groups increase the acidity of carboxylic acids by stabilising the conjugate base. Fluroine is more electronegtive than methyl group.![]()
Sponsor Area
Calculate the number of sigma bonds in diphenyl ketone.

Number of sigma bonds = 25.
Draw the structure and write the name of the position isomer of pentan-3-one.
Structure of pentan-3-one is given below.
Its position isomer is pentan-2-one.
Why is it important to distil out the aldehyde as soon as it is formed by the oxidation of primary alcohol?
What does PCC stand for? Give its composition and one use.
Write the product and name of the following reaction:
Benzyl alcohol + pyridinium chlorochromate
Pyridinium chlorochromate is used in the conversion of primary alcohol to aldehyde.
Ethanal is more soluble in water than ethyl chloride. Explain.
Why is butanone less volatile than ethoxy ethane?
What is the correct order of increasing boiling point?
I: CH3CH2CH2OH,
II:CH3CH2OCH3,
III:CH3CH2CHO,
IV:CH3CH2CH3.
CH3CH2CH3 < CH3CH2OCH3 < CH3CH2CHO < CH3CH2CH2OH
Write an equation for making aldehydes by the oxo-process.
What happens when 3-methyl but-2-ene is treated with ozone and the product is reduced?
When 3-methyl but-2-ene is treated with ozone ozonide is formed which on further reduction gives acetone and acetaldehyde.

What happens when 2-methyl butene-2 is ozonised and this product is reduced?
When 2-methyl butene-2 is ozonised, it forms ozonide compound which on further reduction gives ethanal and propanone.
Write the equation for the reaction when 2,3-dimethyl butene-2 is treated with ozone and the ozonide is reduced.
When 2,3- dimethyl but-2-ene is treated with ozone, it form ozoinde which on further reduction gives propanone and water.
How will you prepare benzaldehyde from phenol?
2. Salicylaldehyde on distillation with zinc dust will form benzaldehyde.

How will you obtain benzophenone from benzene
When benzene is treated with bezoyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride benzophenone is formed.
How will you prepare acetaldehyde from acetylene?
Acetylene in the presence of 42% sulphuric acid followed by mercury sulphate produce acetaldehyde.![]()
Prepare ethanal from ethanoly chloride by reduction method.

Give the industrial preparation of ethanal.
Give the product of the reaction of acetaldehyde with sodium hydrogen sulphite.
When acetaldehyde react with sodium hydrogen sulphite, it gives acetaldehyde bisulphite addition product.
What happens when ethanal reacts with excess of methanol in the presence of trace amount of HCl?
When ethanal reacts with excess of methanol in the presence of trace amount of HCl, it forms 1,1-dimethyl ethane.
Explain Clemmensen’s reduction.

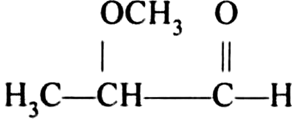
Write the structures of A and B.![]()
When cyclohexanol react with copper at 573 K temperature, it gives cyclohexanonesuch (A) which on further reaction gives cyclohexane such as (B).
Write one distinction test for acetal-dehyde and acetone.

Acetone does not gives silver mirror test.
Sponsor Area
What happens when ethanol is treated with concentrated sulphuric acid
(a) above 0°C, (b) below 0°C?
(a)When ethanol is treated with concentrated sulphuric acid at above 0°C paraldehyde is obtained.
(b) When ethanol is treated with concentrated sulphuric acid at below 0°C meta-aldehyde is obtained.
Mention two important uses of formalin.
(i) It is used for the preservation of biological species.
(ii) It is used in the manufacture of synthetic polymers like bakelite and synthetic dye stuffs like indigo.
Write one reaction to exemplify Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction?
When benzene or substituted benzene is treated with acid chloride in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride, it affords the corresponding ketone. This reaction is known as Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction.
Write one chemical reaction to exemplify Cannizzaro reaction.
Aldehydes which do not have an α-hydrogen atom, undergo self oxidation and reduction (disproportionation) reaction on treatment with concentrated alkali.

What happens when ethanal is distilled with dilute H2SO4 at 273 K?

Which aldehyde smells like bitter almonds? Give its one use.
Give one difference between the paraldehyde and metaldehyde.
Metaldehyde is a cyclic tetramer of CH3CHO and is a white solid. It is commonly used as a pesticide against slugs, snails, and other gastropods.
What type of aldehydes undergo Cannizzaro’s reaction?
Aldehydes which do not have an alpha hydrogen atom, undergo self-oxidation and reduction reaction on treatment with concentrated alkali. In this reaction, one molecule of the aldehyde is reduced to alcohol while another is oxidized to carboxylic acid salt.
For example,

Name the aldehyde used in the preparation of bakelite. Give its one industrial preparation.
Methanal is used in the preparation of bakelite.![]()
Write the reaction between acetyl chloride and dimethyl cadmium.
Acetyl chloride on reaction with dimethyl cadmium formation of acetone take place.
What do you mean by condensation reactions?

Arrange the following in their increasing order of expected enol content.
CH3COCH2CHO, CH3COCH3, CH3CHO, CH3COCH2 COCH3.
Increasing order of expected enol content is given below;
CH3CHO< CH3COCH3<CH3COCH2CHO<CH3COCH2 COCH3
Give a chemical test to distinguish between acetone and acetic acid.
2CH3COOH +Na2CO3 ----> 2CH3COONa + CO2 +H2O
CH3COCH3 +Na2CO3 ----> no reaction
During the formation of acid chloride, which bond C—OH or CO—H of carboxylic acid is broken?
Why carboxylic acids are called fatty acids?
How are formalin and trioxane related to methanol?
Mention a chemical property in which methanoic acid differs from acetic acid.
But-2-en-1, 4-dioic acid exist in two isomeric forms. Write the structure of these two isomers?

How will you synthesise propanoic acid from propylene?
Conversion of propanoic acid from propylene.
![]()
Write the structure and IUPAC name of the product formed:

and IUPAC name is phenyl ethanoic acid.
In the following sequence of reaction, A and B are two unknown compounds. Identify them.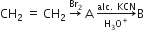
A is 1,2 dibromoethane
B is 1,2 ethane 1,2 dicarboxylic
Convert ethanol into propanoic acid.
Ethanol react with Phosphorus tribromide to form bromo ethane which on further reaction with magnesium in presence of ether form grignard reagent. Further reaction of grignard regent gives propanoic acid.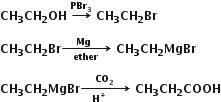
Convert benzene into benzoic acid.

Sponsor Area
What happens when carbon monoxide is added to methanol in the presence of Rh catalyst ?
Carbon monoxide and methanol react in the presence of a homogeneous rhodium catalyst to give acetic acid.
Why carboxylic acids have a higher boiling point than alcohols of same number of carbon atoms?
Arrange the following compounds in order of increasing boiling point :
CH3CH2CH2OH, CH3COCH3,CH3CH2COOH, CH3OCH2CH3.
Propionic acid has stronger hydrogen bond than alcohol therefore the boiling point of propionic acid is higher than others. proponal is more polar than methoxy ethane. Therefore, the intermolecular diopole -dipole attraction is stronger in the methoxyethane. Hence increasing order of boiling point of the given compounds is as follows:
CH3OCH2CH3 < CH3COCH3 < CH3CH2CH2OH < CH3CH2COOH
Ethanoic acid has a molecular mass of 120 in the vapour state. Explain.
Account for the fact that the C–O bond is shorter in RCOOH than in ROH.

Due to this resonance, there is some double bond character in the C—O bond of the acid which shortens the bond length.
Why is carboxylic acid a stronger acid than alcohol?
Account for the fact that chloroacetic acid has a lower pKa value than acetic acid.

Which is a stronger acid and why? Nitroacetic acid or chloroacetic acid?
Which of the following reducing agents can reduce RCOOH → RCH2OH?
NaBH4, LiAlH4, B2H6/H3O+ Na/C2H5OH
What happens when ethanoic acid is heated with P2O5?

What is decarboxylation?
Give a chemical test to distinguish between CH3COOH and HCOOH.
Differentiate between n-pentanol and pentanoic acid.
CH3CH2CH2CH2COOH +NaHCO3 --> CH3CH2CH2CH2COONa +CO2 + H2O
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH +NaHCO3 --> No reaction
Name the reagent which converts benzoic acid into benzene directly.
Why does benzoic acid not undergo Friedel-Craft reaction?
Arrange the following compound in increasing order of their boiling points:
Acetic acid, Methyl formate, Acetamide, Propan-1-ol.
What product is obtained when ethyl benzene is oxidised with alkaline KMnO4?
Of the hydroxy organic compound ROH and R'OH, the first one is basic and the other is acidic in behaviour. How is R different from R' ?
What happens when (CH3)3CCOOH reacts with bromine in the presence of red phosphorus?
What happens when benzoic acid is treated with a mixture of conc.HNO3 and conc. H2SO4?

What happens when propionic acid reacts with thionyl chloride?
CH3CH2COOH + SOCl2 → CH3CH2COCl + SO2 + HCl
Ethanoyl chloride fumes in air. Explain.
CH3COCl + H2O → CH3COOH + HCl.
Which one of FCH2COOH, ClCH2COOH, BrCH2COOH and ICH2COOH is the strongest acid? Give reason.
What happens when ethanoic acid is treated with lithium aluminium hydride?
On treatment withlithium aluminium hydride ethanoic acid is reduced to ethanol. ![]()
Formic acid is not made by oxidative method, why?
Give the common and IUPAC name of the following compounds:
IUPAC name: Benzene cerbaldehyde.
Give the common and IUPAC name of the following compounds:

Common name: Divinyl ketone.
IUPAC name : Pent-1, 4-dien-3-one.
Give name of the reagents to bring about the following transformation:
Hexan-1-ol to hexanal
Give name of the reagents to bring about the following transformation:
Cyclohexanol to cyclohexanone
Give name of the reagents to bring about the following transformation:
p-Fluorotoluene to p-fluorobenzaldehyde
Give name of the reagents to bring about the following transformation:
Ethane nitrile to propanal
Give name of the reagents to bring about the following transformation:
But-2-ene to ethanal.
Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their boiling points:
CH3CH2CH2CHO, CH3CH2CH2CH2OH, H5C2—O—C2H5, CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3.
The molecular masses of these compounds are in the range of 72 to 74. Since only n-butanol molecules are associated due to extensive inter-molecular hydrogen bonding, therefore, the boiling points of n-butanol would be the highest. Butanal is more polar than ethoxy ethane. Therefore, the intermolecular dipole-dipole attraction is stronger in the former. The p-pentane molecules have only weak Van der Waals forces. In view of the above facts the following compounds are arranged as per their increasing order of boiling points.
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3<H5C2—O-C2H5 < CH3CH2CH2CHO < CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
Discuss the bonding of the carbonyl group ?
The carbonyl carbon atom is sp2 -hybridised and forms three sigma bond. The fourth valence electron of carbon remains in its p-orbital and forms pi-bond with oxygen by overlapping with p- orbital of an oxygen. Also, the oxygen atom also has two non bonding electron pairs. Thus the carbonyl carbon and the three atoms attached to it lie in the same plane and the pi-electron is above and below this plane. The bond angle are approximately 1200.
Account for the following:
Ethanal is more soluble in water than ethane but less than the ethanol.

But due to lack of hydrogen available to H-bond O of H2O, ethanal is less soluble in water than ethanol.
Account for the following:
Acetone is completely miscible in water while acetophenone does not.
But due to bulky benzene ring, acetophenone cannot form hydrogen bonds with H2O, hence it is immiscible.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points and give reason.

The boiling points of carbonyl compounds are higher than the non-polar alkanes but lower than that of alcohols of comparable molecular mass. Give reasons.
(i) The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are higher than the boiling points of nonpolar alkanes because dipole-dipole attractions between the molecules of carbonyl compounds are much stronger than the Van der Waals forces which operate between the molecules of alkanes of comparable molecular mass.
(ii) The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are lower than the boiling points of alcohols because the dipole-dipole interactions between the molecules of carbonyl compounds are weaker than the intermolecular hydrogen binding in alcohol molecules of comparable molecular mass.
How will you obtain aldehydes from primary alcohols?
Preparation of aldehydes from primary alcohols:
(i) By the oxidation of alcohols: An aldehyde is prepared when a primary alcohol is oxidised by acidified potassium dichromate under controlled conditions.
(ii) By catalytic dehydrogenation of alcohol: By passing vapours of a primary alcohol over hot reduced copper at 573 K, we get an aldehyde.
How will you prepare ketones from alcohols?
(i) Catalytic dehydrogenation of secondary alcohol.

(ii) Oxidation of secondary alcohol

Discuss the method of preparation of an aldehyde from acid chloride.
Discuss the preparation of aldehydes and ketones from alkenes.
Prepartion of aldehydes:
From acyl chloride (acid chloride):
Acyl chloride is hydrogenated over catalyst, palladium on barium sulphate. This reaction is called Rosenmund reduction.
From nitriles and esters:
Nitriles are reduced to corresponding imine with stannous chloride in the presence of hydrochloric acid which on hydrolysis give corresponding aldehyde.
Prepartion of ketones:
Treatment of acyl chlorides with dialkylcadmium gives ketone.
From benzene or substituted benzenes:
when benzene or substituted benzene is treated with acid chloride in the presece of anhydrous aluminium chloride, it afford the corresponding keton. This reaction is known as Friedel - crafts acylation reaction.
How will you obtain acetophenone from (i) benzene (ii) ethyl benzene (iii) benzoyl chloride?

(ii) Acetophenone from ethyl benzene

(iii) Acetophenone from benzoyl chloride

Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system of nomenclature:
CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH2CHO
Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system of nomenclature:
CH3CH2COCH(C2H5)CH2CH2Cl
Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system of nomenclature:
CH3COCH2COCH3
Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system of nomenclature:
CH3CH(CH3)CH2C(CH3)2 COCH3
Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system of nomenclature:
(CH3)3CCH2COOH.
Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system of nomenclature:
OHCC6H4CHO-p
Write the IUPAC names of the following ketones and aldehydes. Wherever possible, give also common names.

Write the IUPAC names of the following ketones and aldehydes. Wherever possible, give also common names.

Write the IUPAC names of the following ketones and aldehydes. Wherever possible, give also common names.

Common name: Beta-phenynolacrolein
Write the IUPAC names of the following ketones and aldehydes. Wherever possible, give also common names.
PhCOPh
Common Name: Benzophenone
Draw structures of the following derivatives:
The 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone of benzaldehyde
Structure of 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone.
![]()
Draw structures of the following derivatives:
Acetaldehydedimethyl acetal
Structure of Acetaldehydedimethyl acetal
Which of the following compounds would undergo aldol condensation, which the Cannizzaro reaction and which neither? Write the structures of the expected products of aldol condensation and Cannizzaro reaction.
(i) Methanal
(ii) 2-Methylpentanal
(iii) Benzaldehyde
(iv) Benzophenone
(v) Cyclohexanone
(vi) 1-Phenyl propanone
(vii) Phenyl acetaldehyde
(viii) Butan-1--ol
(ix) 2, 2-Dimethyl butanal.


Cannizzaro reaction: (i), (iii), (ix). The products are:

Neither: [iv], [viii].
How will you convert ethanal into the following compounds?
But-2-enal

where pcc stands for ‘Pyridinium chloro chromate.
How will you convert ethanal into the following compounds?
But-2-enoic acid.
Conversion of but -2-enoic acid from ethanol.
Write structural formulae and names of the four possible aldol condensation products from propanal and butanal. In each case, indicate which aldehyde served as nucleophile and which as electrophile.
Case i) Aldol condensation in two molecules of butanal, in which one acts as a nucleophile and the other as an electrophile.

Case ii) Aldol condensation in two molecules of propanal, in which one acts as nucleophile and other as an electrophile.

Case iii) Aldol condensation in between of one molecule of propanal and butanal in which propanal acts as a nucleophile and butanal acts as an electrophile.


An organic compound with the molecular formula C9H10O forms 2, 4-DNP derivative, reduces Tollen’s reagent and undergoes Cannizzaro reaction. On vigorous oxidation, it gives 1, 2-benzenedicarboxylic acid. Identify the compound.
The given molecular formula C9H10O forms 2,4 –DNP derivative and reduces tollen’s reagent. Therefore, the given compound must be an aldehyde. Again the compound undergoes cannizzaro reaction and on oxidation gives 1,2 –benzenedicarboxylic acid. Therefore, the –CHO group is directly attached to a benzene ring and this benzaldehyde is ortho-substituted. Hence, the compound is 2-ethylbenzaldehyde.

The above mechanism is given as,

An organic compound (A) (Mol. formula C8H16O2) was hydrolysed with dilute sulphuric acid to give a carboxylic acid (B) and an alcohol (C). Oxidation of (C) with chromic acid produced (B). Write equations for the reactions involved.
The given molecular formula C8H16O2 gives carboxylic acid (B) and an alcohol (C) on hydrolysis with H2SO4. Thus, compound may be an ester. Further, alcohol C gives acid B on oxidation with chromic acid.Thus, B and C must contain equal number of carbon atoms. As given compound contain 8 carbon atom, each B and C must contain 4 atom. On dehydration, alcohol C gives but-2-ene. Therefore, C is of straight chain and hence, it is butan-1-ol.
On oxidation, butan-1-ol givers butanoic acid. Hence, acid B is butanoic acid. Therefore the given compound is ester is butylbutanoate.
![]()
The above statement is explained as,


Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated:
Acetaldehyde, Acetone, Di-tert-butyl ketone, Methyl tert-hutyl ketone (reactivity towards HCN).
HCN is nucleophile, attack of nucleophile is easier if the steric hindrance is lesser. In the given compound, the +I effect increase hence reactivity of HCN towards these compound decreases thus, the order is,
Di-tert-butyl ketone < Methyl tert-butyl ketone < Acetone < Acetaldehyde.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated:
CH3CH2CH(Br)COOH, CH3CH(Br)CH2COOH, (CH3)2CHCOOH, CH3CH2CH2COOH (acid strength).
The compound having +I effect will decrease the strength of the acids and groups having –I effect will increase the strength of the acids. In the given compounds the alkyl group has +I effect and Br- group has –I effect. Hence, the strength of the given acids increase as;
(CH3)2CHCOOH < CH3CH2CH2COOH < CH3CH(Br)CH2COOH < CH3CH2CH(Br)COOH.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated:
Benzoic acid, 4-Nitrohenzoic acid, 3, 4-Dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-Methoxy benzoic acid (acidstrength).
The +I effect (electron –donating) groups decrease the strengths of acids, while –I (electron withdrawing) groups increase the strength of acids. As methoxy group is an electron-donating group, 4-methoxybenzoic acid is a weaker acid than benzoic acid. Nitro groups is an electron withdrawing groups and will increase the strength of acids. As 3, 4-dintrobenzoic acid contains two nitro groups, it is a slightly stronger acid than 4-nitrobenzoic acid. Hence, the strength of the given acid increase as:
4-Methoxy benzoic acid < Benzoic acid < 4-Nitrobenzoic acid < 3, 4-Dinitrobenzoic acid.
Give simple tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
Propanal and Propanone
Give simple tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
Phenol and Benzoic acid
C6H5COOH + NaHCO3 → C6H5COONa + CO2 ↑ + H2O
C6H5OH + NaHCO3 → No reaction
Give simple tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one

Give simple tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
Ethanal and propanal
Propanal does not give iodoform test.
Give simple tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
Acetophenone and Benzophenone
Give simple tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate
Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate:
(a) Benzoic acid produces effervescence with NaHCO3 solution while ethyl benzoate does not.
(b) Benzoic acid produces vapours of benzene when heated with soda lime (CaO + NaOH) while ethyl benzoate does not.
Give simple tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone.

How will you bring about the following conversions in not more than two steps?
Propanone to propene

How will you bring about the following conversions in not more than two steps?
Ethanol to 3-Hydroxy butanal

How will you bring about the following conversions in not more than two steps?
Benzaldehyde to Benzophenone.

How will you bring about the following conversions in not more than two steps?
Benzaldehyde to 3-Phenylpropan-1-ol

How will you bring about the following conversions in not more than two steps?
Benzoic acid to m-Nitrobenzyl alcohol.

How will you bring about the following conversions in not more than two steps?
Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde

How will you bring about the following conversions in not more than two steps?
Benzene to m-Nitroacetophenone
Benzene to m-Nitro acetophenone:

How will you bring about the following conversions in not more than two steps?
Bromo benzene to 1-Phenyl ethanol.
Bromo benzene to 1-Phenyl ethanol:

Describe the following:
Acetylation
Acetylation: The introduction of an acetyl functional group into an organic compound is known as acetylation. This reaction carried out in the presence of a base such as pyridine. In this reaction acetyl group substitute an active hydrogen atom. Acetyl chloride and acetic anhydride are commonly used as acetylating agent.

Describe the following:
Cannizzaro reaction
Describe the following:
Cross aldol condensation

Describe the following:
Decarboxylation.
Carboxylic acids lose carbon dioxide to form hydrocarbons when their sodium salts are heated with sodalime(NaOH and CaO in the ration of 3:1). The reaction is known as decarboxylation. 
Give plausible explanation for each of the following:
Cyclohexanone forms cyanohydrin in good yield but 2, 2, 6-trimethyl cyclohexanone does not.

Centre of nucleophile attack by CN- .The presence of three methyl group (which are electron repelling) reduces the polarity of > C = O group on one hand and after a steric hindrance to nucleophilic attack of CN-at > C = O group. Therefore, trimethyl cyclohexanone does not give good yield i.e., it gives very poor yield.
Give plausible explanation for each of the following:
There are two –NH2 groups in semicarbazide. However, only one is involved in the formation of semicarbazones.

Give plausible explanation for each of the following:
During the preparation of esters from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst, the water or the ester should be removed as fast as it is formed.

The nature of reaction, esterification of carboxylic acid, is reversible as ester formed reacts with water and produces reactants and thus an equilibrium is set up between reactants and products. The removal of ester or water shifts the equilibrium to right according to Le-Chatelier’s principle and more and more ester is formed.
Explain the following:
p-Hydroxy benzaldehyde is more soluble in water than o-hydroxy benzaldehyde.
Explain the following:
Benzaldehyde does not undergo aldol condensation whereas acetaldehyde does.
Explain the following with one suitable example in each case:
Wolff-Kishner reduction.

Explain the following with one suitable example in each case:
Clemmensen-reduction

Write reactions for obtaining:
Acetone from acetic acid
Acetic acid react with calcium hydroxide to form calcium acetate which on dry distillation gives acetone and calcium carbonate.
Draw the structure of carbonyl group and indicate clearly:
(i) The hybridised state of carbon.
(ii) σ and  bonds present and
bonds present and
(iii) the electrophilic and nucleophilic centres.
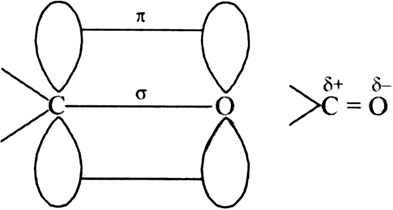
(i) sp2 hybridization of carbon.
(ii) σ and
(iii) C is nucleophilic centre.
O is electrophilic centre.
How will you perform the following conversions?
Ethanal into lactic acid.
Conversion of Ethanal into lactic acid.

How will you perform the following conversions?
Ethanal into pent-3-en-one.
Conversion of ethanal into pent-3-en-one.![]()

How does the reaction with NaHCO3 helps in purifying CH3CHO?

This can be achived by the decomposing the adduct by acid to generate pure ethanal leaving behind the impurities.

Convert:
Ethyne into 1, 1-dimethoxy ethane
Ethyne react with dilute sulphuric acid in presece of mercury sulphate which gives ethanal. Ethanal on further reaction with methanol in the presence of acid (HCl) gives 1,1-dimethoxy ethane.
Convert:
Ethyne into propanone.
Ethyne react with liquid ammonia followed by methyl chloride gives propyne which on further reaction with dilute sulphuric acid in the presence of mercury sulphate gives propanone.
Organic compound A(C3H8O) gives brisk effervescence with Na metal and on reaction with Cu at 573 K gives B (C3H6O). Compound B gives a yellow ppt. with I2 and alkali B on reaction with semicarbazide gives C. what are the structures of compounds A, B and C? Write all reactions involved.
Organic compound A is an alcohol as it gives a reaction with Na metal and contains one oxygen.
B is either an aldehyde or ketone but as it gives yellow ppt. with I2/NaOH, it is a ketone, CH3COCH3. Therefore A is a secondary alcohol.


Organic compound A(C5H10O), capable of being resolved into optical isomers gives a yellow precipitate with 2, 4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine
(i) Write the structure and IUPAC name of organic compound A.
(ii) What happens when this organic compound ‘A’ reacts with diamine silver (I) ion in alkaline medium?

ii) When 2-methyl react with diamine silver (I) ion in alkaline medium, it gives silver mirror test.

Explain haloform reaction.
Methyl Ketones CH3COR on oxidation with X2/NaOH (X = Cl, Br, I) gives sodium salt of carboxylic acid with one carbon atom less. The CH3 group bonded to carbonyl group is converted to haloform, CHX3'. With iodine in NaOH, a yellow precipitate of iodoform CHI3 is obtained (iodoform test).
How will you make the following conversions?
Benzoic acid into 2-phenyl propan-2-ol.
Benzoic acid react with methanol in presence of acid and gives acetophenone which on further reaction with grignard reagent gives 2-phenyl propan-2-ol.
What are aldehydes and ketones? How acetone and acetaldehyde can be prepared from CH3COCl ?
Prepartion of acetone and acetaldehyde from CH3COCl.

How acetaldehyde and acetone can be prepared from alcohols by oxidation and dehydrogenation?
(i) By oxidation: With KMnO4 or K2Cr2O7

(ii) By dehydrogenation: With copper at 573 K.

Identify (A), (B) and (C) in the following reaction:


A is calcium acetate
B is Acetone
C is Aetone hydrazone
Explain the mechanism of aldol condensation using ethanal as an example.

Account for the following:
Carboxylic acids with five or less carbons are water soluble, but many with six or more carbons dissolves in alcohols.

The R group is non-polar and hydrophobic and this effect dominates when R possess more than five carbon. Thereby, decreasing its solubility in more polar solvent as water, but the solubility in less polar solvent such as alcohol increases.
Account for the following:
Carboxylic acids exist as dimers in the vapour phase.
Illustrate the mechanism of reaction of carbonyl group with an ammonia derivative, H2N—Z.

The reaction is an addition-elimination reaction.
Account for the fact that the C—O bond in RCOOH is shorter than in ROH ?

Due to this resonance, there is some double-bond character in the C—O bond of the acid, which shortens its bond length.
In case of ROH,there is no any resonating structure thus C-O bond is larger in it.
Compare the reactivities of the C = O in RCOOH and RCHO towards nucleophiles.

Why is benzoic acid a stronger acid than phenol?

The conjugate base of phenol, a phenoxide ion, has non-equivalent resonance structures in which the negative charge is at the less electronegative carbon atom. Thus, the benzoate ion is more stable than phenoxide ion. Hence, benzoic acid is a stronger acid than phenol.

Write equation for the ionization of RCOOH and for Ka and then explain why RCOOH has a lower pKa value than alcohol.
Equation for the ionization of RCOOH is,
RCOOH is a stronger acid and has a lower pKa value than alcohol because RCOO- is more resonance stabilized than RO- ion.![]()
Account for the following acidic strength order:

Account for the following acidic strength order:

Account for the following acidic strength order:

Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated:
CH3CH2CH(Br)COOH, CH3CH(Br)CH2COOH, (CH3)2CHCOOH, CH3CH2CH2COOH (acidic strength)
The compound having +I effect (electron donating group) will decrease the strength of the acids and groups having –I effect (electron withdrawing group) will increase the strength of the acids. In the given compounds the alkyl group has +I effect and Br- group has –I effect. Hence, the strength of the given acids increase as;
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated:
Benzoic acid, 4-Nitrobenzoic acid, 3, 4-Dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-Methoxybenzoic acid (acid strength)
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated:
Benzoic acid, 4-nitrobenzoic acid, 2-nitrobenzoic acid, 2-Methyl benzoic acid (acid strength).
An organic compound contains 69.77% carbon, 11.63% hydrogen and rest oxygen. The molecular mass of the compound is 86. It does not reduce Tollen’s reagent but forms an addition compound with sodium hydrogensulphite and give positive iodoform test. On vigorous oxidation it gives ethanoic and propanoic acid. Write the possible structure of the compound.
|
Element |
% |
At. Mass |
Reactive no. of atoms |
Simplest ratio |
|
Carbon |
69.77 |
12 |
69.77/12=5.8 |
5.8/1.16=5 |
|
Hydrogen |
11.63 |
1 |
11.63/1=11.63 |
11.63/11.6=10 |
|
Oxygen |
18.6 |
16 |
18.6/16=1.16 |
11.6/11.6=1 |
Empirical formula = C5H10O
Empirical formula mass=5 x 12+10x 1+16= 60+10+16=86
Molecular mass= 86
n = molecular formula mass /empirical formula mass
= 86/86 = 1
Molecular formula = C5H10O
Structure of the compound CH3CH2COCH2CH3
Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion, carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol. Why?

What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case.
Cyanohydrin

What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case.
Acetal
Acetal: In acetal two alkoxy groups are present on the terminal carbon atom. One bond is connected to an alkyl group and other is connected to a hydrogen atom.
On reaction of aldehyde and monohydric alcohol in the presence of dry HCl gas, hemiacetals are produced which on further reaction with one more molecule of alcohol yield acetal.

What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case.
Semicarbazone

What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case.
Aldol

What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case.
Hemiacetal

What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case.
Oxime
Oximes are class of organic compounds having the general formula RR’CNOH, where R is an organic side chain and R’ is either hydrogen or an organic side chain. If R’ is H, then it is known as aldoxime and If R’ is an organic side chain, it is known as ketoxime. On treatment with hydroxylamine in a weakly acidic medium, aldehydes or ketones form oximes.
What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case.
Ketal

What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case.
Imine

What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case.
2, 4-DNP-derivative
2,4 dinitrophenylhydrazine are 2,4 –DNP – derivatives, which are produced when aldehyde or ketones react with 2,4-dinitropheylhydrazine in a weekly acidic medium. 2, 4-DNP-derivatives are yellow, orange or red solids, useful for characterisation of aldehydes and ketones.

What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case.
Schiff’s base
Explain the following:
Aldehydes are more reactive than the isomeric ketones.
Explain the following:
Acetaldehyde, CH3CHO, does not undergo Cannizzaro reaction.
Explain the following:
Aldehydes undergo oxidation more readily than the ketones.
Explain the following:
Hydrazones of aldehydes and ketones are not prepared in highly acidic medium.
Explain the following:
Butanal and butanol have almost the same solubility in water, yet, their boiling points differ widely.
Describe the following:
Protonation

Describe the following:
Fehling’s reagent
On heating with an aldehyde with Fehling's regent, a reddish brown precipitate is obtained.
Describe the following:
Tollen’s reagent
Describe the following:
Acetylation

Describe the following:
Trans-esterification.

Explain the reason why:
Carbon-oxygen bond lengths in formic acid are 1.23 Å and 1.36 Å, but both the carbon-oxygen bonds in sodium formate have the same value, 1.27 Å.

Explain the reason why:
Acetic acid can be halogenated in the presence of red P and Cl2 but formic acid cannot be halogenated in the same way.
Explain the reason why:
Formic acid is stronger than acetic acid.
On other hand HCOOH formic acid does not have any electron releasing group thus removal of proton is easier. Thus, formic acid is stronger than acetic acid.
Explain the reason why:
The carboxylate ion, RCOO- is more stable than the carboxylic acid, RCOOH.

Explain the reason why:
Carboxylic acids, despite the presence of C = O group in the molecule, do not form oximes, hydrazones, etc.

The conversion of propone into propane using N2H4/glycol-KOH is known as _______ reduction.
Ethyl formate on reaction with excess of CH3MgBr followed by hydrolysis gives ________.
State whether the following statements are True or False:
A.
Benzaldehyde undergoes aldol conden-sation in alkaline medium.B.
Aldol condensation is given by all alde-hydes and ketones.C.
Ethanoyl chloride on reaction with H2/Pd gives ethanal.D.
Aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition reaction.E.
Acetaldehyde and propionaldehyde can be distinguished by using an iodoform test.B. FALSE
C. FALSE
D. TRUE
E. TRUE
State whether the following statements are True or False:
A.
Benzaldehyde gives Cannizzaro reaction as it does not have any α-hydrogen.B.
The boiling point of propanoic acid is lesser than that of butano1-1.C.
Formic acid does not reduce Tollen’s reagent.D.
All the C—O bond lengths in carboxylate ion are identical.E.
Acetate ion is stronger base than methoxide ion.B. FALSE
C. FALSE
D. TRUE
E. FALSE
Cannizzaro reaction is not given by
- trimethyl acetaldehyde
- acetaldehyde
- benzaldehyde
- formaldehyde
B.
acetaldehydeWhat is the main reason for the fact that carboxylic acid can undergo ionisation?
- Absence of α-hydrogen
- Higher reactivity of α-hydrogen
- Resonance stabilisation of carboxylate ion
- Hydrogen bonding
C.
Resonance stabilisation of carboxylate ionBenzyl alcohol is obtained from benzaldehyde by
- Wurtz reaction
- Cannizzaro reaction
- Claisen reaction
- Perkin reaction
B.
Cannizzaro reactionWhat happens when acid chloride is reduced with LiAlH4?
When acid chloride is reduced with LiAlH4 , it give aldehyde.

What type of aldehydes undergo Cannizzaro’s reaction?
Aldehydes which do not have an α-hydrogen atom, undergo cannizzaro's reaction on treatment with concentrated alkali such as (KOH and NaOH).
During preparation of esters from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of acid catalyst water or ester formed should be removed as soon as it is formed.
The formation of esters from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of acid catelyst in a reversible reaction.
![]()
To shift the equilibrium in forward direction, the water or ester formed should be removed as fast as it is formed.
What happens when calcium formate is distilled?
When calcium formate is distilled, formaldehyde is formed.
Give the reaction of acetone with semicarbazide.
When acetone react with semicarbazide, it forms semicarbazone.

Name the product when benzophenone is reduced with Zn(Hg) in the presence of HCl.
When benzophenone is reduced with Zn(Hg) in the presence of HCl, it gives diphenyl methane. This reaction is also known as clemmensen reduction.

How does benzaldehyde react with CH3MgI followed by water?
When benzaldehyde react with CH3MgI, it gives 1-phenyl ethanol.

How will you distinguish between phenol and benzoic acid?
Phenol react with ferric chloride and forms iron phenol complex which is violet is colour . benzoic acid does not give this test.

Why does methanal not give aldol condensation while ethanol gives?
Methanol does not give aldol condensation because only those compounds which have α-hydrogen atoms can undergo aldol reaction ethanol pessess α-hydrogen and undergoes aldol condensation Methanal has no alpha hydrogen atoms hence does not undergo aldol condensation.
Why is benzaldehyde is less reactive than acetaldehyde towards nucleophilic addition reactions?
C-atom of Carbonyl group of benzaldehyde is less electrophilic than C-atom of Carbonyl group in acetaldehyde. Polarity of Carbonyl group is in bonzaldehyde reduced due to resonance making it less reactive in nucleophillic addition reactions.

Account for the following:
(i) Formaldehyde gives Cannizzaro’s reaction whereas acetaldehyde does not.
(ii) Carboxylic acids do not give characteristic reactions of carbonyl compounds.
i) Aldehydes which have an alpha hydrogen atom does not give cannizzaro's reaction. Acetaldehyde, CH3CHO has 3 hydrogens but in case of formaldehyde, HCHO there is no alpha hydrogen present , hence formaldehyde undergoes cannizzaro's reaction where as acetaldehyde does not.
ii) Caroboxylic acids do not give characteristic reaction of carbonyl compounds. This is because the lone pairs on oxygen atoms attached to hydrogen atom in the –COOH group are involved in resonance there by making carbon atom less available.
Account for the following:
(i) Chloroacetic acid has higher pKa value than acetic acid.
(ii) Electrophilic substitution in benzoic acid takes place at meta position.
(iii) Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than alcohols of comparable molecular masses.
i) Chloroacetic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid and has a higher value of dissociation constant Ka than that of acetic acid. We know that pKa= -log Ka, it means that chloroacetic acid having higher value Ka will have lower value of pKa, chloroacetic acid is stronger than acetic acid because Cl group is electron withdrawing and chloroacetate ion is more stabilised than acetate ion.![]()
ii) Carboxyl group (-COOH) is electron withdrawing i.e deactivating the benzene ring and thus electron density becomes very less at ortho and para position in comparison to meta position. Electrophiles (+vely charged species) find it easier to attack at meta position as there is higher electron density this-COOH group is meta directing.
as there is a positive charge on ortho and para position, the electron density is higher at meta position and hence electrophilic substitution takes place at meta position.
iii) Carboxylic group (-COOH ) in acid is highly polar and generally, exist as dimers containing two hydrogen bond each as shown below:

These hydrogen bonds in carboxylic acid are stronger than those in alcohols. It is due to following two factors
a) the O-H bond of the carboxylic acids are more strongly polarised due to the adjacent electron-attracting >C=O groups.
b) the oxygen atom of the group >C=O in carboxylic acid is more negative as compared to the oxygen atom of the alcohol.

Thus carboxylic acids possesses higher boiling point than corresponding alcohols of similar molecular masses.
How would you obtain the following named sources:
(i) Tertiary butyl alcohol from acetone? (ii) Acetone from acetic acid?
Mention conditions for reactions involved.
i)
ii) acetic acid is first converted to its calcium salt which si then subjected to dry distillation.
Explain why O-hydroxy benzaldehyde is a liquid at room temperature while p- hydroxy benzaldehyde is a high melting solid.
Due to intramolecular H-bonding in O-hydroxy benzaldehyde exists as discrete molecule whereas due to intermolecular H-bonding p-hydroxy benzaldehyde exist as associated molecules. To break this intermolecular H-bonds a large amount of energy is needed. Consequently P-isomer has a much higher m.p. and b.p. than that of O-isomer. As a result O-hydroxy benzaldehyde is liquid.
Describe the following with an example:
Aldol condensation
Aldehydes and ketones having at least one α-hydrogen condense in the presence of dilute alkali as catalyst to form β-hydroxy alddil ehydes (aldol) or β-hydroxy ketones (ketol).
Sodium Bisulphite is used for the purification of aldehydes and Ketones. Explain ?
Aldehydes and Ketones form addition compounds with NaHSO3 whereas impurities do not. On hydrolysis we get pure aldehydes and Ketones back.

Explain with suitable example:
(i) Clemenson reduction, (ii) Wolff-Kishner reduction.
i) Clemenson reduction : The carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketone is reduced to –CH2 group on treatment with zinc amalgam and conc. Hydrochloric acid.

ii) wolff- kishner reduction : On treatment with hydrazine followed by heating with sodium or potassium hydroxide in high boiling solvent like ethylene glycol.

How would you distinguish between pentanal and diethyl ketone?
Pentanal (CH3CH2CH3CH2CHO) and aldehyde reduces tollen's reagent and Fehling's solution.
Diethyl ketone (CH3CH2COCH2CH3) does not.
what happens when (CH3)3CCOOH reacts with bromine in the presence of red Phosphorous ?
No reaction, No HVZ reaction, (CH3)3CCOOH does not have any alpha hydrogen necessary for the reaction.
How would you distinguish between acetophenone and benzophenone?
Acetophenone on reaction with sodium hypoidite give iodoform (yellow ppt). Benzophenone does not give this test.

Give one use of benzene-1,4 dicarboxylic acid.
Benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid is used in the preparation of terelene.
What happens when formaldehyde is treated with ammonia?
When formaldehyde is treated with ammonia, it forms urotropine.
What happens when acetaldehyde is react with benzaldehyde with strong aqueous alkali solution ?
When acetaldehyde react with bezaldehyde with strong alkali solution, it forms 3-pheylprop-2-en-1-al.
What happens when formaldehyde is treated with conc.NaOH solution?
When formaldehyde is treated with conc.NaOH solution, it forms of methanol and sodium formate.
discuss hell -vollhard -zelinsky reaction (HVZ) ?
Carboxylic acids having an α – hydrogen are halogenated at the α –position on treatment with chlorine or bromine in the presence of small amount of red phosphorus to give α –halocarboxylic acids.
Discuss Rosenmud's reaction.
Acyl chlorides when hydrogenated over catalyst, palladium on barium sulphate yield aldehydes.

Out of acetophenone and benzophenone, which gives iodoform test ? Write the reaction involved. (The compound should have CH3CO-group to show the iodoform test.)
Acetophenone (C6H5COCH3) contains the grouping (CH3CO attached to carbon) and hence given iodoform test while benzophenone does not contain this group and hence does not give iodoform test.

Write the equation involved in the acetylation of Salicylic acid.
Acetylation of Salicylic acid:

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(i) Benzaldehyde and Benzoic acid
(ii) Propanal and Propanone
Benzaldehyde and Benzoic acid
Test-1 Through sodium bicarbonate Benzaldehyde does not react with sodium bicarbonate. However, benzoic acid will produce brisk effervescence on reaction with sodium bicarbonate as shown in the given reaction:
C6H5COOH + NaHCO3 ---> C6H5COONa + H2O + CO2
Test-2 Through, Tollen's reagent Benzaldehyde reacts with an ammoniacal solution of silver nitrate to form a silver mirror.
C6H5CHO + 2[Ag(NH3)2]+ + 3OH- --> C6H5COO- + 2Ag + 2H2O + 4NH3
However, no such reaction is given by benzoic acid.
(ii) Test-1 Iodoform Test
Propanone gives positive iodoform test, as it contains CH3CO group, whereas propanal does not give iodoform test. The reaction is as follows:
![]()
Account for the following:
(i) CH3CHO is more reactive than CH3 COCH3 towards reaction with HCN.
(ii) The carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol.
(i) CH3COCH3 is sterically hindered than CH3CHO due to the presence of alkyl group on both sides of the carbonyl carbon, making them less reactive towards nucleophilic attack because both methyl groups have electron releasing tendency due to -I effect. These alkyl groups make ketone less reactive by donating an electron to a carbonyl group. Therefore, acetaldehyde is more reactive towards reaction with HCN.
(ii) Carboxylic acids are acidic due to resonance stabilisation of carboxylate anion and in phenols, the acidic character is present due to resonance stabilisation of phenoxide anion. Carboxylic acids are more acidic than phenols because the negative charge in carboxylate anion is more spread out compared to the phenoxide ion, as there are two electronegative O-atoms in carboxylate anion compared to one in phenoxide ion. In the resonance structures of carboxylate anion, the negative charge is present on the O-atoms, while in the resonance of phenoxide ion, a negative charge is also present on the electropositive carbon atom, which leads to less stability of phenoxide ion than carboxylate anion.
How will you bring about the following conversions?
(i) Propanone to propane
(ii) Benzoyl chloride to benzaldehyde
(iii) Ethanal to but-2-enal
(i) Conversion of Propanone to Propane:

(ii) Conversion of Benzoyl chloride to benzaldehyde:

(iii) On treatment with dilute alkali, ethanol produces 3-hydroxybutanal gives But-2-enal on hheating.

Illustrate the following name reaction giving suitable example in each case:
(i) Clemmensen reduction
(ii) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction
(i) Clemmensen Reduction
The carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones is reduced to the CH2 group on treatment with zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid. This is known as Clemmensen reduction.
![]()
(ii) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky (HVZ )reaction.
Carboxylic acids having a ![]() hydrogen are halogenated at the
hydrogen are halogenated at the ![]() position on treatment with chlorine or bromine in the presence of small amount of red phosphorus to give
position on treatment with chlorine or bromine in the presence of small amount of red phosphorus to give ![]() halocarboxylic acids. The reaction is known as Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction.
halocarboxylic acids. The reaction is known as Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction.

illustrate the following reactions giving a suitable example for each.
(i) Cross aldol condensation
(ii) Decarboxylation
i) Cross aldol condensation: The reaction between an aldehyde/ketone and a carbonyl compound lacking an alpha-hydrogen (cross aldol condensation) is called the Claisen-Schmidt condensation. It gives a mixture of four products.

ii) Decarboxylation refers to the reaction in which carboxylic acids lose carbon dioxide to form hydrocarbons when their sodium salts are heated with soda-lime.

Give simple tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds
(i) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one
(ii) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone
(iii) Phenol and Benzoic acid
i) Pentan-2-one and pentan-3-one can be distinguished by iodoform test.
Pentan-2-one is a methyl ketone. Thus, it responds to this test. But pentan-3-one not being a methyl ketone does not respond to this test.

ii) Benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) and acetophenone (C6H5COCH3) can be distinguished by iodoform test. Acetophenone, being a methyl ketone on treatment with I2/NaOH undergoes iodoform reaction to give a yellow ppt. of iodoform. On the other hand, Benzaldehyde does not give this test.

iii) Phenol and benzoic acid can be distinguished by ferric chloride test.
Ferric chloride test:
Phenol reacts with neutral FeCl3 to form ferric phenoxide complex giving violet coloration.
6C6H5OH + FeCl3 ---> [Fe (OC6H5)6]3-+3H++3Cl-
Phenol iron-phenol complex
(Violet color)
But benzoic acid reacts with neutral FeCl3 to give a buff-coloured precipitate of ferric benzoate.
![]()
Explain the following giving one example for each:
(i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
(ii) Friedel Craft’s acetylation of anisole.
i) Reimer-Tiemann Reaction: Reimer-Tiemann reaction involves the treatment of phenol with chloroform in the presence of aqueous sodium hydroxide at 340 K followed by hydrolysis of the resulting product to give 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde (salicylaldehyde). The chemical reaction can be represented as follows.

ii) Friedel-Crafts acetylation of anisole: Friedel-Crafts acetylation of anisole involves the treatment of anisole with either acetyl chloride or acetic anhydride to give 2-methoxyacetophenone (as a minor product) and 4-methoxyacetophenone (as a major product).
The chemical reaction can be represented as follows.

Give chemical tests to distinguish between
(i) Propanal and propanone,
(ii) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone.
(b) How would you obtain
(i) But-2-enal from ethanal,
(ii) Butanoic acid from butanol,
(iii) Benzoic acid from ethylbenzene?
(i) Propanal (CH3CH2CHO) can be distinguished from propanone (CH3COCH3) by iodoform test.
Being a methyl ketone, propanone on treatment with I2/NaOHundergoes iodoform reaction to give a yellow ppt. of iodoform

(ii) Benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) and acetophenone (C6H5COCH3) can be distinguished by iodoform test.

Acetophenone, being a methyl ketone on treatment with I2 /NaOH undergoes iodoform reaction to give a yellow ppt. of iodoform. On the other hand, benzaldehyde does not give this test.
b)
i)

ii) ![]()
iii)

(a) Describe the following giving linked chemical equations:
(i) Cannizzaro reaction
(ii) Decarboxylation
(b) Complete the following chemical equations:

(i) Cannizaro reaction
In this reaction, the aldehydes which do not have a -hydrogen atom, undergo self-oxidation and reduction (disproportionation) reaction on treatment with a concentrated alkali.
Example:

(ii) Decarboxylation
The decarboxylation reaction can be carried out either by using soda lime or by electrolysis
Using soda lime: Sodium salts of carboxylic acids when heated with soda lime (NaOH + CaO) in the ratio 3:1) undergo decarboxylation reaction to yield alkanes.
![]()
Electrolytic decarboxylation: Electrolysis of aqueous solutions of sodium or potassium salts of carboxylic acids give alkanes having twice the number of carbon atoms present in the alkyl group of acid.
This is known as Kolbe’s decarboxylation.
2RCOONa--> 2RCOO- + 2Na+
H2O-->2OH- + 2H+
At Anode:-
2RCOO- - 2e---> CO2 + R - R
At Cathode:-
2H+ + 2e----> H2
b)

A compound 'A' of molecular formula C2H3OCl undergoes a series of reactions as shown below. Write the structures of A, B, C and D in the following reactions:
![]()
(b) Distinguish between the following:
(i) C6H5-COCH3 and C6H5 - CHO
(ii) Benzoic acid and methyl benzoate
(c) Write the structure of 2- methylbutanal.
On carrying hydrogenation of A in the presence of poisoned palladium, we get an aldehyde. Hence, B can be Ethanal, CH3CHO.
An aldehyde, on treating with dilute alkali, undergoes aldol condensation reaction. Hence, C can be CH3CH (OH) CH2CHO.
On heating an aldol product, it loses water to produce a double bond and we get CH3CH=CHCHO.
Hence, we have

(b)
(i) Acetophenone has methyl group attached to carbonyl carbon while benzaldehyde does not. Therefore, we can use iodoform test to distinguish between the two. Acetophenone will undergo iodoform test and give a yellow precipitate.
C6H5-COCH3 ![]() C6H5COOH + CHI3
C6H5COOH + CHI3
Acetophenone (yellow ppt.)
C6H5CHO ![]() No reaction
No reaction
Benzaldehyde
(ii) Benzoic acid can react with sodium bicarbonate to give brisk effervescence due to the release of CO2, while methyl benzoate does not.
C6H5COOH + NaHCO3----> C6H5COONa + H2O + CO2
Benzoic acid (brisk effervescence)
C6H5COOCH3 + NaHCO3---> No reaction
Methyl benzoate
(c) The Structure of 2- methylbutanal is:

(a) Write the structures of the main product when acetone ( CH3-CO-CH3) reacts with the following reagent:
(i) Zn-Hg/conc. HCl
(ii) H2N-NHCONH2/H+
(iii) CH3MgBr and then H3O+
(a) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their boiling point:
C2H5OH, CH3-CHO, CH3-COOH
(b) Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds:
CH3CH2CHO and CH3CH2COCH3
(i) Acetone undergoes clemmensen reduction in presence of zinc amalgam and conc.HCl to give propane.
![]()
(ii) Acetone reacts with semicarbazide to form semicarbazone.

(iii) Acetone reduces to form tertiary alcohol in the presence of Grignard reagent.

(b) Due to extensive hydrogen bonding, carboxylic acid has the highest boiling points an among the given compound. Alcohols, with a smaller number of the hydrogen bond, have a lesser boiling point. Aldehydes have least boiling point due to the absence of hydrogen bonding.
Hence the order of boiling point is:
CH3-CHO < C2H5OH < CH3COOH
(c) 2- Butanone has a methyl group attached to carbonyl carbon unlike propanal .hence , it can give iodoform test.
CH3CH2COCH3 ![]() CH3CH2COOH + CHI3
CH3CH2COOH + CHI3
(Yellow ppt.)
CH3CH2CHO ![]() No reaction
No reaction
Propanal
Write the equations involved in the following reactions:
(i) Reimer - Tiemann reaction
(ii) Williamson’s ether synthesis
(i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction:

(ii) Williamson’s ether synthesis:
When alkyl halide is reacted with sodium alkoxide it gives ether
R-X + R’ – ONa -----> R – O - R’ + NaX
Alkyl halide sodium alkoxide ether
An example is a reaction of sodium ethoxide with chloroethane to form diethyl ether and sodium chloride.
Na+C2H5O- + C2H5Cl ---> C2H5OC2H5 + Na+Cl-
(a) How will you convert the following?
(i) Propanone to Propan-2-ol
(ii) Ethanal to 2-hydroxy propanoic acid
(iii) Toluene to benzoic acid
(b) Give simple chemical test to distinguish between:
(i) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one
(ii) Ethanal and Propanal
(a)
(i) Propanone to Propan-2-ol
![]()
(ii) Ethanal to 2-Hydroxypropanoic acid

(iii) Toluene to benzoic acid.

(b)
(i) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one

By Iodoform Test
Pentan-2-one being a methyl ketone when treated with NaOI (I2/NaOH) gives yellow precipitate of iodoform but pentan-3-one does not.


(ii) Ethanal and Propanal
![]()
By Iodoform test
Ethanal containing group CH3-C=O linked to H, reacts with I2/NaOH (or NaOI) to give yellow precipitate of iodoform but propanal does not contain group CH3-C=O linked to H or C and hence does not react with I2/NaOH to give yellow precipitate.


(a) Write the products of the following reactions:

(b) Which acid of each pair shown here would you expect to be stronger?
(i) F — CH2 —COOH or Cl — CH2 — COOH
(ii) 
(a)
(i)
![]()
This reaction is Clemmensen reduction.
(ii)

This reaction is Rosenmunds reduction.
(iii)

This reaction is an electrophilic substitution reaction.
(b)
(i) F — CH2 — COOH is a stronger acid than Cl — CH2 — COOH because F is more electronegative than Cl so it will favour the release of H+ ion faster by dragging the electron density towards itself more as compared to Cl.
(ii) Acetic acid is a stronger acid than phenol. On losing a proton, carboxylic acid forms carboxylate ion and phenol forms phenoxide ion. The negative charge is delocalized in both the molecules. The conjugate base of the carboxylic acid has two resonance structures (shown below) in which negative charge is delocalized over two oxygen atoms which stabilises the carboxylate ion.

On the other hand, in phenoxide ion, the negative charge is delocalized over entire molecule on the less electronegative carbon atom as given below.
Thus resonance in phenoxide is not important as compared to resonance in carboxylate ion.
Further, in carboxylate ion, the negative charge is effectively delocalized over two oxygen atoms whereas it is less effectively delocalized over one oxygen atom and the less electronegative carbon atom in phenoxide ion.

Thus acetic acid is a stronger acid than phenol.
(a) Write a suitable chemical equation to complete each of the following transformations:
(i) Butan-1-ol to butanoic acid
(ii) 4-methylacetophenone to benzene-1, 4-dicarboxylic acid
(b) An organic compound with molecular formula C9H10O forms 2, 4-DNP derivative, reduces Tollen’s reagent and undergoes Cannizzaro’s reaction. On vigorous oxidation, it gives 1, 2-benzenedicarboxylic acid. Identify the compound.
(i) Butanoic acid can be obtained by oxidation of butan-1-ol.
The most common reagent used for oxidation of alcohols is chromium (Vl) reagents including chromic acid (H2CrO4), potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) and chromic anhydride (CrO3).

(ii) 4- methylacetophenone can be converted to benzene-1, 4- dicarboxylic acid as follows:

(b) It is given that the compound (with molecular formula C9H10O) forms 2, 4-DNP derivative and reduces Tollen’s reagent. Therefore, the given compound must be an aldehyde.
Again, the compound undergoes Cannizzaro reaction and on oxidation gives 1, 2-benzenedicarboxylic acid. Therefore, the -CHO group is directly attached to a benzene ring and this benzaldehyde is ortho-substituted. Hence, the compound is 2-ethylbenzaldehyde.

2 – ethyl bezaldehyde
The given reactions can be explained by the following equations.

(a) Give chemical tests to distinguish between
(i) Propanol and propanone
(ii) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone
(b) Arrange the following compounds in an increasing order of their property as indicated:
(i) Acetaldeyde, Acetone, Methyl tert-butyl ketone (reactivity towards HCN)
(ii) Benzoic acid, 3, 4-Dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-Methoxybenzoic acid (acid strength).
(iii) CH3CH2CH (Br) COOH, CH3CH (Br) CH2COOH, (CH3)2CHCOOH (acid strength)
(a)
(i) Propanone gives iodoform test while propanol does not give this test.

(ii) Benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) and acetophenone (C6H5COCH3) can be distinguished by iodoform test.
Acetophenone, being a methyl ketone on treatment with I2/NaOH undergoes iodoform reaction to give a yellow ppt. of iodoform. On the other hand, benzaldehyde does not give this test.

(b)
(i) Methyl tert-butyl ketone < Acetone < Acetaldehyde
When HCN reacts with a compound, the attacking species is a nucleophile, CN-.Therefore, as the negative charge on the compound increases, its reactivity with HCN decreases. In the given compounds, the +I effect increases as shown below. It can be observed that steric hindrance also increases in the same.

(ii) 4-Methoxybenzoic acid < Benzoic acid < 3, 4-Dinitrobenzoic acid
Electron-donating groups decrease the strengths of acids, while electron-withdrawing groups increase the strengths of acids. As methoxy group is an electron-donating group, 4-ethoxybenzoic acid is a weaker acid than benzoic acid. Nitro group is an electron-withdrawing group and will increase the strengths of acids.
(iii) (CH3)2 CHCOOH < CH3CH(Br)CH2COOH < CH3CH2CH(Br)COOH
After losing a proton, carboxylic acids gain a negative charge as shown:
R – COOH ---> R - COO- + H+
Now, any group that will help stabilise the negative charge will increase the stability of the carboxyl ion and as a result, will increase the strength of the acid. Thus, groups having +I effect will decrease the strength of the acids and groups having -I effect will increase the strength of the acids. In the given compounds, -CH3 group has +I effect and Br- group has -I effect. Thus, acids containing Br- are stronger.
The -I effect grows weaker as distance increases. Hence, CH3CH(Br)CH2COOH is a weaker acid than CH3CH2CH(Br)COOH.
Write the structures of A, B, C, D and E in the following reactions:
Or
(a)Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved in Cannizzaro reaction.
(b)Draw the structure of the semicarbazone of ethanal.
(c)Why pKa of F-CH2-COOH is lower than that of Cl−CH2−COOH?
(d)Write the product in the following reaction:
![]()
(e)How can you distinguish between propanal and propanone?

Or

d)

e)
|
Propanal |
Propanone |
|
It forms silver mirror on reaction with Tollen's reagent. |
It is not oxidised by Tollen's reagent. |
|
It does not react with iodoform. |
It gives positive iodoform test. |
|
On reacting with Schiff's reagent, it gives pink colour. |
It does not react with Schiff's reagent. |
i) Mn Shows the highest oxidation state of +7 with oxygen but with fluorine it shows the highest oxidation state of +4.
ii) Cr2+ is a strong reducing agent.
iii) Cu2+ salts are coloured while Zn2+ salts are white.
b) Complete the following equations:

i) Mn Shows the highest oxidation state of +7 with oxygen but with fluorine, it shows the highest oxidation state of +4 because of the ability of oxygen to form multiple bonds with Mn metal.
ii) Cr2+ is strongly reducing in nature. It has a d4 configuration. Cr2+ is a stronger reducing agent because it can lose one of its electrons to become Cr3+ in which the t2g level of d-orbital is half filled and the eg level is empty.which is a more stable configuration.
iii) The electronic configuration of Zn = 3d10 4s2
Zn2+ = 3d10
where as the electronic configuration of Cu = 3d10 4s1
Cu2+ =3d9
In the case of Zn fully filled d orbital is present therefore no d-d transition can be possible in this case and it is colourless.
In the case of copper 3d9 because of d-d transition electrons emits light in the visible range and hence they are coloured compounds.
b)


b)
Distinguish between:
i) C6H5-COCH3 and C6H5-CHO
ii) CH3COOH and HCOOH
c) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their boiling points:
CH3CHO,CH3COOH,CH3CH2OH
Or
a) Write the chemical reaction involved in Wolff Kishner reduction.
b) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction:
C6H5COCH3, CH3-CHO, CH3COCH3
c) why carboxylic acid does not give reactions of carbonyl group ?
d) Write the product in the following reaction
e) A and B are two functional isomers of compound C3H6O. On heating with NaOH and I2, isomers B forms a yellow precipitate of iodoform whereas isomer A does not form any precipitate. Write the formulae of A and B.

b)
(i)Heat both compounds with NaOH and I2, C6H5COCH3 forms yellow ppt of CHI3 whereas C6H5CHO does not.
(ii)Add ammoniacal solution of silver nitrate (Tollen’s reagent) to both the compounds, HCOOH gives silver mirror but CH3COOH does not.
C) CH3CHO < CH3CH2OH < CH3COOH
Or
a) 
b)C6H5COCH3 < CH3COCH3 < CH3CHO
(c) Because of resonance in the carboxylic group the carbonyl group loses a double bond character.
d) 
e) A : CH3CH2CHO B : CH3COCH3
Draw the structure of 4-chloropentan-2-one ?
The structure of 4-chloropentan-2-one is as follows:![]()
Rearrange the compounds of each of the following sets in order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement:
(i) 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane, 2-Bromopentane
(ii) 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 3-Bromo-2-methylbutane
(iii) 1-Bromobutane, 1-Bromo-2, 2-dimethylpropane, 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane(i) 1-Bromopentane > 2-Bromopentane > 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane
(ii) 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane > 3-Bromo-2-methylbutane > 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane
(iii) 1-Bromobutane >1-Bromo-2-methylbutane >1-Bromo-2, 2-dimethylpropane.
How would you obtain the following?
(i) Benzoquinone from phenol
(ii) 2-methyl propan-2-ol from methyl-magnesium bromide
(iii) Propane-2-ol from propene
(i) Phenol is oxidised to benzoquinone as

It is an oxidation reaction. The ready oxidation of phenol is explained by the fact that the presence of OH group on the benzene ring increases electron density to the ring due to resonance which makes it for the oxidation reaction.
(ii)

(iii) If the propene is allowed to react with water in the presence ofan acid as catalyst, then propan-2-ol is obtained.
![]()
(a) Illustrate the following name reactions:
(i) Cannizzaro’s reaction
(ii) Clemmensen reduction
(b) How would you obtain the following?
(i) But-2-enal from ethanal
(ii) Butanoic acid from butanol
(iii) Benzoic acid from ethylbenzene
OR
(a) Given chemical tests to distinguish between the following:
(i) Benzoic acid and ethyl benzoate
(ii) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone
(b) Complete each synthesis by giving missing reagents or products in the following:

(i) Cannizaro reaction
In this reaction, the aldehydes which do not have a a-hydrogen atom, undergo self -oxidation and reduction (disproportionation) reaction on treatment with a concentrated alkali.
Example:

(ii) Clemmensen reduction
In this reaction, the carbonyl compounds are reduced in presence of zinc amalgam to give the corresponding alkane.
![]()
(b)
(i) But-2-enal from ethanal

(ii) Butanoic acid from butanol

(iii) Benzoic acid from ethylbenzene

Or
(a)
(i) Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate can be distinguished by sodium bicarbonate test.
Sodium bicarbonate test:
Acids react with NaHCO3 to produce brisk effervescence due to the evolution of CO2gas.Benzoic acid being an acid responds to this test, but ethyl benzoate does not.

(ii) Benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) and acetophenone (C6H5COCH3) can be distinguished by iodoform test.
Acetophenone, being a methyl ketone on treatment with I2/NaOH undergoes iodoform reaction to give a yellow ppt. of iodoform. On the other hand, benzaldehyde does not give this test.

b)

(a) Write the products formed when CH3CHO reacts with the following reagents:
(i) HCN
(ii) H2N−OH
(iii) CH3CHO in the presence of dilute NaOH
(b) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(i) Benzoic acid and Phenol
(ii) Propanal and Propanone
OR
(a) Account for the following:
(i) Cl−CH2COOH is a stronger acid than CH3COOH.
(ii) Carboxylic acids do not give reactions of the carbonyl group.
(b) Write the chemical equations to illustrate the following name reactions:
(i) Rosenmund reduction
(ii) Cannizzaro's reaction
(c) Out of CH3CH2−CO−CH2−CH3 and CH3CH2−CH2−CO−CH3, which gives iodoform test?
(i) Acetaldehyde (CH3CHO) reacts with hydrogen cyanide HCN to give 2-Hydroxypropapanenitrile as product.

(ii) Acetaldehyde (CH3CHO) reacts with Hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to give acetaldoxime as a product.
![]()
(iii) The reaction of acetaldehyde with acetaldehyde in the presence of dilute NaOH, this is the kind of Aldol reaction by which obtained 3-hydroxybutanal as a product. Further, proceed reaction when using heat in the reaction, its gives aldol condensation product which is But-2-enal.

(b) Chemical tests to distinguish the following compounds:
(i) Benzoic acid and Phenol : Benzoic acid and phenol can be distinguished by FeCl3 tests. Both reacts with FeCl3 to give different colours. Phenol reacts with FeCl3 to give violet coloured precipitate while benzoic acid gives buff coloured precipitate.
3C6H5OH +FeCl3 ---> (C6H5O)3Fe + 3HCl
phenol violet colour
3C6H5COOH +FeCl3 ---> (C6H5COO)3Fe +3HCl
Benzoic acid buff colour
(ii) Propanal and Propanone : These two are distinguished by the iodoform test.propanal does not give iodoform test when it reacts with I2 in the presence of NaOH while propanone give iodoform test when reacts with I2 in the presence of NaOH.
CH3COCH3 +3NaOI --> CHI3 + CH3COONa +2NaOH
Propane Yellow ppt
CH3CH2OH +NaOI ---> No ppt of CH3I formed
Or
a) (i) Cl-CH2COOH is a stronger acid than CH3COOH :
Substitution of electron withdrawing group on carboxylic acid affect the acidity of the carboxylic acid. Chlorine is a electron withdrawing group and its increase the acidity of carboxylic acids by stabilising the conjugate base due to delocalisation of the negative charge by resonance effects.
Chloroacetic acid ( Cl-CH2COOH) pKa value is equal to 2.7, while pKa value of acetic acid (CH3COOH) is equal to 4.7.
(ii) In carboxylic acid presence of lone pairs of electrons on oxygen which are involves in resonance due to this the electrophilic character of carbon in carboxylic acid decreases. So due to such reason carboxylic acid does not show the characteristic reaction of the carbonyl group.

b)
i)
ii)
C )
Pentan-2-one (CH3-CH2-CH2-CO-CH3) give yellow precipitate of CHI3 with NaOI, that means it gives iodoform test.
CH3-CH2-CH2-CO-CH3 + 3NaOI --> CHI3 + CH3CH2COONa + 2NaOH
Yellow
ppt.
Pentan-3-one (CH3-CH2-CO-CH2-CH3) does not give yellow precipitate with CHI3 with NaOI, so Pentan-3-one does not give iodoform test.
Do the following conversions in not more than two steps :
Benzoic acid to benzaldehyde
conversion of the benzoic acid to benzaldehyde
![]()
pKa value of 4-nitrobenzoic acid is lower than that of benzoic acid.
It is due to e– with drawing nature of –NO2 attach at the para position of Benzene due to which tends to lose H+ ion increases and acidic character increases.
(A), (B) and (C) are three non-cyclic functional isomers of a carbonyl compound with molecular formula C4H8O .
Isomers (A) and (C) give positive Tollen’s test whereas isomer (B) does not give Tollen’s test but gives positive Iodoform test. Isomers (A) and (B) on reduction with Zn(Hg)/conc. HCl give the same product (D).
(a) Write the structures of (A), (B), (C) and (D)
(b) Out of (A), (B) and (C) isomers, which one is least reactive towards addition of HCN ?
(a)

(b) Since (B) is ketons so it will be less reactive towards nucleophilic addition reaction with HCN due to +I effect & steric hindrance
Write the reactions involved in the following :
Hofmann bromamide degradation reaction
Here R = Alkyl group
Ar = Aryl group
2-chloro-2-methylpentane on reaction with sodium methoxide in methanol yields:

-
Both a and c
-
Only c
-
Both a and b
-
All of these
D.
All of these
Strong nucleophile ![]() polar solvent (MeOH) gives elimination products Products over substitution products but all products are possible in different yields.
polar solvent (MeOH) gives elimination products Products over substitution products but all products are possible in different yields.
Which compound would give 5-keto-2-methyl hexanal upon ozonolysis?
B.



5-Keto-2-methyl hexanal
In the following sequence of reaction,
![]()
The Product C is
-
C6H5COOH
-
C6H5CH3
-
C6H5CH2OH
-
C6H5CHO
D.
C6H5CHO
Toluene undergoes oxidation with KMnO4, forms benzoic acid. In this conversation, alkyl part of toluene converts into the carboxylic group. Further, the benzoic acid reacts with thionyl chloride (SOCl2) to give benzoyl chloride which upon reduction wth H2/Pd or BaSO4 forms benzaldehyde (Rosenmund reduction).
The reactions are
The most suitable reagent for the conversion of
R-CH2 -OH →R- CHO is
-
KMnO4
-
K2Cr2O7
-
CrO3
-
PCC (pyridinium chlorochromate)
D.
PCC (pyridinium chlorochromate)
Pyridinium chlorochromate is the mild oxidising agent which causes conversion of alcohol to aldehyde stage, While others cause conversion of alcohol to acid.
Sodium phenoxide when heated with CO2 under pressure at 125oC yields a product which on acetylation products C.
![]()
A.

It is a Kolbe Schmidt reaction.

The second step of the reaction is an example of acetylation reaction.
In the reaction,
![]()
The product C is
-
acetaldehyde
-
acetylene
-
ethylene
-
acetyl chloride
C.
ethylene
LiAlH4 causes reduction
PCl5 causes chlorination
Trichloroacetaldehyde was subjected to Cannizzaro's reaction by using NaOH. The mixture of the products contains sodium trichloroacetate ion and another compound. The other compound is
-
2, 2, 2-Trichloroethanol
-
Trichloromethanol
-
2, 2, 2-Trichloropropanol
-
Chloroform
A.
2, 2, 2-Trichloroethanol
The Cannizzaro product of given reaction yields 2, 2, 2-trichloroethanol.
The strongest acid amongst the following compounds is
-
CH3COOH
-
HCOOH
-
CH3CH2CH(Cl)CO2H
-
ClCH2CH2CH2COOH
C.
CH3CH2CH(Cl)CO2H
α-chlorobutyric acid is more stronger acid than others due to - I effect of Cl.
Ozonolysis of an organic compound gives formaldehyde as one of the products. This confirms the presence of,
-
two ethylenic double bonds
-
a vinyl group
-
an isopropyl group
-
an acetylenic triple bond
B.
a vinyl group

Presence of one vinyl group gives formaldehyde as one of the product in ozonolysis.
Silver Mirror test is given by which one of the following compounds? -
Acetaldehyde
-
Acetone
-
Formaldehyde
-
Benzophenone
Acetaldehyde
Acetone
Formaldehyde
Benzophenone
A.
Acetaldehyde
C.
Formaldehyde


Thus (a) acetaldehyde and (c) formaldehyde give silver mirror test.
One mole of a symmetrical alkene on ozonolysis gives two moles of an aldehyde having a molecular mass of 44 u. The alkene is
-
Propene
-
1-butene
-
2-butene
-
ethene
C.
2-butene
(a) The general formula of aldehyde compound is CnH2nO. First, calculate the value of n.
(b) Alkene is symmetrical, therefore, only single type of aldehyde is produced as a product.
CnH2nO = 44
CnH2n = 44-16 = 28
n = 2
Therefore, since, the alkenes is symmetrical, then the structure is
CH3 - CH=CH -CH3
Thus, ![]()
The major product obtained in the following reaction is
B.

DIBAL – H is electrophilic reducing agent reduces cynide, esters, lactone, amide,carboxylic acid into corresponding Aldehyde (partial reduction)
In Cannizzaro reaction given below ![]() the slowest step is
the slowest step is
-
The attack of
 at the carboxyl group
at the carboxyl group -
The transfer of hydride to the carbonyl group
-
The abstraction of proton from the carboxylic group
-
The deprotonation of PhCH2OH
B.
The transfer of hydride to the carbonyl group
Hydride transfer is the slowest step.

The best reagent to convert pent -3- en-2-ol into pent -3-en-2-one is
-
Acidic permanganate
-
Acidic dichromate
-
Chromic anhydride in glacial acetic acid
-
Pyridinium chloro – chromate
C.
Chromic anhydride in glacial acetic acid
The major product of the following reaction is,

A.


The reaction is a dehydrohalogenation E2-elimination reaction. Elimination takes place in single step and proceed by formation of transition state from anti position.
Which of the following salts is the most basic in aqueous solution?
Pb(CH3COO)2
Al(CN)3
CH3COOK
FeCl3
C.
CH3COOK
CH3COOK is most basic among the given salts.
The correct statement regarding a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha -carbon, is
-
a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha -carbon rapidly equilibrates with its corresponding enol and this process is known as aldehyde-ketone equilibration.
-
a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon rapidly equilibrates with its corresponding enol and this process is known as carbonylation
-
a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon rapidly equilibrates with its corresponding enol and this process is known as keto-enol tautomerism
-
a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha carbon never equilibrates with its corresponding enol
C.
a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon rapidly equilibrates with its corresponding enol and this process is known as keto-enol tautomerism
In keto-enol tautomerism. a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha -carbon rapidly equilibrates with the corresponding enol.
Which of the following reagents would distinguish cis-cyclopenta-1-,2-diol from the trans isomer?
-
Ozone
-
MnO2
-
Aluminium isopropoxide
-
Acetone
D.
Acetone
Cis-cyclopenta-1,2-diol when reacts with acetone forms cyclic ketal whereas trans-isomers of cyclopenta-1,2 diol cannot form cyclic ketal.
Treatment of cyclopentanone

methyl lithium gives which of the following species?
-
Cyclopentanonyl anion
-
Cyclopentanonyl cation
-
Cyclopentanonyl radical
-
Cyclopentanonyl biradical
A.
Cyclopentanonyl anion

Here, CH3Li abstract is an active proton from cyclo pentanone forming methane leaving behind an intermediate lithium cyclopentanoyl anion.
Given,
Which of the given compounds can exhibit tautomerism?
-
I and II
-
I and III
-
II and III
-
I, II and III
D.
I, II and III
In keto-enol tautomerism, keto form should have alpha hydrogen (structure I and II).
An organic compound X having molecular formula C5H10O yields phenyl hydrazone and gives negative response to the iodoform test and tollen test. It produces n -pentane on reduction X could be
-
pentanal
-
2-pentanone
-
3-pentanone
-
n -amyl alcohol
C.
3-pentanone
since the compound X yields phenyl hydrazone and gives a negative response to the iodoform test and tollen 's test. it must contain a C=O group but is neither a methyl ketone nor an aldehyde. having molecular formula C5H10O
Which one is most reactive towards nucleophilic addition reaction?
D.

Reactivity of carbonyl compounds towards nucleophilic addition reactions depends on the presence of substituted group.Electron withdrawing (-I,-M) group increased reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction thus correct order is 
The reaction by which benzaldehyde cannot be prepared?
-
 +CrO2Cl2 and CS2 followed by H3O+
+CrO2Cl2 and CS2 followed by H3O+
-
 +H2 in presence of anhydrous AlCl3.
+H2 in presence of anhydrous AlCl3.
-
 +CO +HCl in presence of anhydrous AlCl3
+CO +HCl in presence of anhydrous AlCl3
-
 +Zn/Hg and Conc. HCl
+Zn/Hg and Conc. HCl
D.

Thus, from the reagents given in option (d) benzaldehyde is not obtained
CH3CHO and C6H5CH2CHO can be distinguished chemically by
-
Benedict test
-
Iodoform test
-
Tollen's reagent test
-
Fehling solution test
B.
Iodoform test
CH3CHO and C6H5CH2CHO both being aliphatic aldehydes react with Tollen's reagent, Fehling solution and Benedict solution. So, these reagents cannot be used to distinguish them. CH3CHOreacts with NaOH and I2 to give yellow crystals of iodoform while C6H5CH2CHO does not react with it.
CH3CHO +3I2 4 NaOH → CHI3 +HCOONa +3NaI +3H2O
C6H5CH2CHO +I2 +4NaOH → No reaction
Thus, CH3CHO and C6H5CH2CHO can be distinguished by iodoform test.
Predict the products in the given reaction,
C.

When benzaldehyde is treated with 50% alkali, it undergoes oxidation to give an acid salt as well as a reduction to give an alcohol. This reaction is called Cannizzaro's reaction.
Acetone is treated with an excess of ethanol in the presence of hydrochloric acid. The product obtained is.
D.

When carbonyl compounds are treated with alcohol, they form hemiacetal (hemiketal and acetal/ketal.)
The correct order of decreasing acid strength of trichloroacetic acid (A), trifluoroacetic acid (B), acetic acid (C) and formic acid (D) is
-
B > A> D > C
-
B > D > C > A
-
A> B > C > D
-
A > C > B > D
A.
B > A> D > C
If an electron withdrawing group (-I showing group) is present, it makes the removal of proton more easy by stabilising the remaining carboxylate ion and thus, makes the acid more acidic. The order of acidity of given compounds is

Consider the following reaction
The product 'A' is
-
C6H5CHO
-
C6H5OH
-
C6H5COCH3
-
C6H5Cl
A.
C6H5CHO
In Rosenmund reaction, acid chloride reacts with H2 in the presence of Pd/BaSO4 to yield aldehyde.

Which of the following compounds will give a yellow precipitate with iodine and alkali?
-
Acetophenone
-
Methyl acetate
-
Acetamide
-
2-hydroxylpropane
D.
2-hydroxylpropane
Out the given compounds only (2-hydroxypropane) gives a yellow precipitate with iodine. But other does not give this test. 
Clemmensen reduction of a ketone is carried out in the presence of which of the following?
-
Zn -Hg with HCl
-
LiAlH4
-
H2 and Pt as catalyst
-
Glycol with KOH
A.
Zn -Hg with HCl
The reducing agent used in Clemmensen reduction is Zn - Hg and HCl.
![]()
A reaction of a carbonyl compound with one of the following reagents involves nucleophilic addition followed by the elimination of water. The reagents is
-
a Grignard reagent
-
hydrazine in presence of feebly acidic solution
-
hydrocyanic acid
-
sodium hydrogen sulphite
C.
hydrocyanic acid
Reaction of carbonyl compounds with ammonia derivatives give addition product followed by the elimination reaction. Slightly acidic medium generate a nucleophilic centre for the attack of weak base like ammonia derivatives.
Which of the following compounds undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction most easily? 






A.
 has electron withdrawing group - NO2 which reduces the double bond character between carbon of benzene ring and chlorine. Thus, the correct order of nucleophilic substitution reactions.
has electron withdrawing group - NO2 which reduces the double bond character between carbon of benzene ring and chlorine. Thus, the correct order of nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Match the compounds given in the list I with List II and select the suitable option using the code given below.
|
|
List I |
|
List II |
|
A. |
Benzaldehyde |
1. |
Phenolphtalein |
|
B. |
Phthalic anhydride |
2. |
Benzoin Condensation |
|
C. |
Phenyl benzoate |
3. |
Oil of wintergreen |
|
D. |
Methyl salicylate |
4. |
Fries rearrangement |
-
ABCD4132
-
A
B C D 4 2 3 1 -
A
B C D 2 3 4 1 -
A
B C D 2 1 4 3
D.
|
A
|
B | C | D |
| 2 | 1 | 4 | 3 |
A. Benzoin condensation: When an ethanolic solution of benzaldehyde is heated with a strong alkali like KCN or NaCN, we get benzoin.
B. Formation of Phenolphthalein: When phenol is treated with a pthalic anhydride in the presence of concentrated H2SO4, it gives phenolphthalein, an indicator.
C. Fries rearrangement: When phenyl benzoate heated with anhydrous AlCl3 in the presence of inert solvent gives ortho and para - hydroxy benzophenone. In this rearrangement, there is a benzoyl group migration from the phenolic oxygen to an ortho and para - position.
D. Methyl salicylate: A chief constituent of oil of wintergreen
Which one of the following esters gets hydrolysed most easily under alkaline conditions?
A.

Electron withdrawing group attach to the benzene ring increases the reactivity towards nucleophilic substitution reaction, Since, -NO2 group is strong electron withdrawing group. Hence, in basic medium ester containing -NO2 group will be hydrolysed most easily.
Acetamide is treated with the following reagents separately. Which one of these would yield methylamine?
-
NaOH - Br2
-
Sodalime
-
Hot conc. H2SO4
-
PCl5
A.
NaOH - Br2
The reagent which can convert -CONH2 group into - NH2 group is used for this reaction.
Among the given reagents only NaOH/ Br2 converts -CONH2 group to -NH2 group, thus it is used for converting acetamide to methylamine. This reaction is called Hoffman bromide reaction.
CH3CONH2 + NaOH +Br2 --> CH3NH2 +NaBr + Na2CO3 + H2O
Among the given compounds, the most susceptible to nucleophilic attack at the carbonyl group is
-
CH3COOCH3
-
CH3CONH2
-
CH3COOCOCH3
-
CH3COCl
D.
CH3COCl
Lesser the electron density of acyl carbon atom, more will be the susceptibility of a nucleophile to attack it.
The Cl atom has strong - I effect and weakest +R effect because of the weak π-bond between the small sized C- atom and large sized Cl atom. Thus, in CH3COCl, acyl carbon has least electron density and hence, more susceptible for nucleophilic attack.
H2COH. CH2OH on heating with periodic acid gives
-
2CO2
-
2HCOOH
-

-

D.
Periodic acid is a mild oxidising agent, hence oxidises alcohol into aldehyde.
Propionic acid with Br2-P yields a dibromo product. Its structure would be
-
CH2Br - CHBr -COOH
-

-
CH2-Br-CH2-COBr
-

D.

Br2 in presence of P attacks on the alpha carbon atom of acid and alpha hydrogen is substituted by bromine.
This reaction is called Hell -Volhard Zelinsky (HVZ) reduction.
Acetophenone when reacted with a base, C2H5ONa, yields a stable compound which has the structure
A.

Aldehydes or ketones with the alpha-H atom, in presence of the dilute base, undergoes aldol condensation to give Beta-hydroxy aldehyde or beta-hydroxy ketone. On heating, aldol eliminates water molecule to form alpha, beta unsaturated compound.
The relative reactivities of acyl compounds towards of nucleophilic substitution are in the order of
-
Acyl chloride> Acid anhydride> Ester> Amide
-
Ester > Acyl chloride> Amide > Acid anhydride
-
Acid anhydride > Amide > Ester> Acyl chloride
-
Acyl chloride > Ester > Acid anhydride > Amide
A.
Acyl chloride> Acid anhydride> Ester> Amide
The ease of nucleophilic substitution is depended upon the nature of leaving the group. When the leaving tendency of a group in a compound is high, then the compound is more reactive towards nucleophilic substitution.
The nucleophilic acyl substitution is completed in two-step as shown below.
The reactivity of the compound may be explained on the basicity of the leaving group. A weaker base is a better leaving group. The basicity order is as:
Cl- < RCOO- < RO- < NH-2
Hence, the order of leaving tendency is
and therefore, the order of reactivity of acyl compounds is as:
Acyl chloride >Acid ayhdride > Ester > Amide
Which of the following represents the correct order of the acidity in the given compounds?
-
H3CCOOH > BrCH2COOH > ClCH2COOH > FCH2COOH
-
FCH2COOH > CH3COOH >BrCH2COOH > ClCH2COOH
-
BrCH2COOH > ClCH2COOH > FCH2COOH >CH3COOH
-
FCH2COOH > ClCH2COOH >BrCH2COOH > CH3COOH
D.
FCH2COOH > ClCH2COOH >BrCH2COOH > CH3COOH
The acidity of halogenated acid increases proportionately with the increase in electronegativity of the halogen present. So, the correct order is:
FCH2COOH > ClCH2COOH >BrCH2COOH > CH3COOH
Reduction of aldehydes and ketones into hydrocarbons using zinc amalgam and conc. HCl is Called:
-
Clemmensen reduction
-
Cope reduction
-
Dow reduction
-
Wolff- Kishner reduction
A.
Clemmensen reduction
Clemmensen reduction: Aldehydes and ketones are reduced to the corresponding alkanes by means of amalgamated zinc and HCl
> C=O + 4[H] → >CH2 + H2O
Which of the compounds with molecular formula C5H10 yields acetone on ozonolysis?
-
2-methyl-2- butene
-
3- methyl -1-butene
-
cyclopentane
-
2-methyl-1-butene
A.
2-methyl-2- butene
2-methyl 2-butene (molecular formula C5 H10 ) yields acetone on ozonolysis
Which one of the following on treatment with 50% aqueous sodium hydroxide yields the corresponding alcohol and acid?
-
C6H5CH2CHO
-
C6H5CHO
-
CH3CH2CH2CHO
-
CH3-CO-CH3
B.
C6H5CHO
Aldehydes which do not have and alpha hydrogen atom when heated with a conc. a solution of NaOH undergoes a simultaneous oxidation and reduction (disproportionation) forming a salt of carboxylic acid and alcohol called Cannizzaro reaction.
![]()
The product formed in aldol condensation is:
-
a beta-hydroxy acid
-
a beta -hydroxy aldehyde or ketone
-
an alpha -hydroxy aldehyde or ketone
-
an alpha, beta unsaturated ester
B.
a beta -hydroxy aldehyde or ketone
Condensation between two molecules of an aldehyde or a ketone having at least one alpha -hydrogen atom in presence of a base to form a beta- hydroxy aldehyde or beta - hydroxy ketone is known as aldol condensation.
In a set of reactions, propionic acid yielded a compound D.
![]()
The structure of D would be:
-
CH3CH2CH2NH2
-
CH3CH2CONH2
-
CH3CH2NHCH3
-
CH3CH2NH2
D.
CH3CH2NH2
For reaction,

Hence, compound 'D' is CH3-CH2-NH2
Consider the reactions :
-
A-Methoxymethane, X-Ethanoic acid, Y-Acetate ion, Z-hydrazine
-
A-Methoxymethane, X-Ethanol, Y-Ethanoic acid, Z-Semicarbazide
-
A-Ethanal, X-Ethanol, Y-But-2-enal, Z-Semicarbazone
-
A-Ethanol, X-Acetaldehyde, Y-Butanone, Z-Hydrazone
C.
A-Ethanal, X-Ethanol, Y-But-2-enal, Z-Semicarbazone
Since 'A' gives positive silver mirror test, therefore, it must be an aldehyde or α-hydroxy ketone.
Reaction with semicarbazide indicates that A can be an aldehyde or ketone.
Reaction with OH– i.e., aldol condensation (by assuming alkali to be dilute) indicates that A is aldehyde as aldol reaction of ketones is reversible and carried out in special apparatus.
The IUPAC name of the compound
-
3-keto-2-methylhex-4-enal
-
5-formylhex-2-en-3-one
-
5-methyl-4-oxohex-2-en-5-al
-
3-keto-2-methylhex-5-enal
A.
3-keto-2-methylhex-4-enal

Aldehydes get higher priority over ketone and alkene in numbering of principal C-chain.
therefore 3-keto-2-methylhex-4-enal
Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular mass. It is due to their
Formation of intramolecular H-bonding
Formation of intermolecular H-bonding
Formation of intermolecular H-bonding
More extensive association of carboxylic acid via Vander Waals force of attraction
C.
Formation of intermolecular H-bonding
Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular mass. This is due to the more extensive association through intermolecular H-bonding.

Compound A, C8H10O, is found to react with NaOI (produced by reacting Y with NaOH) and yields a yellow precipitate with characteristic smell. A and Y are respectively
D.

Haloform reaction is shown by compound having

Cannizzaro reaction is not shown by


CH3CHO
HCHO
C.
CH3CHO
The aldehyde/ketone, those do not contain alpha-H atom, show Cannizzaro reaction.
In CH3CHO, the carbonyl group is attached to C- atom having alpha- Hydrogen; Hence, CH3CHO do not show Cannizzaro reaction.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area